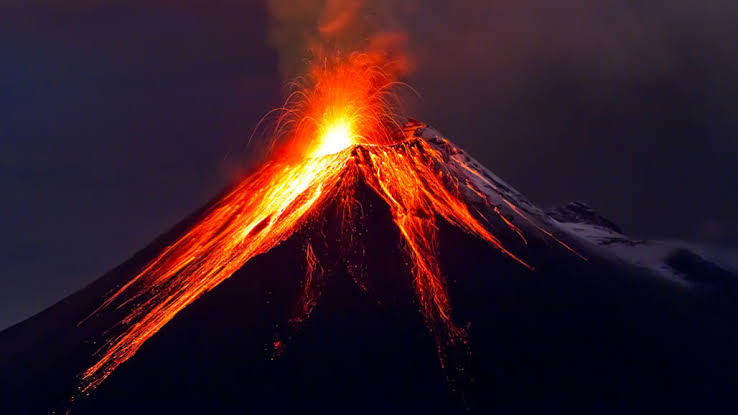
Volcanoes are some of the most dramatic and awe-inspiring natural phenomena on Earth. These fiery mountains have shaped the planet’s landscapes, influenced climate patterns, and even impacted the course of human civilizations. From the slow, steady lava flows of shield volcanoes to the explosive eruptions of stratovolcanoes, each volcanic event tells a story of the Earth’s dynamic interior and the forces that shape life on the surface. Understanding volcanoes requires an exploration of geology, atmospheric science, ecology, and human history, revealing how these natural features play a vital role in shaping our world.
How Volcanoes Form: The Science Behind the Fire
Volcanoes form when molten rock, or magma, from the Earth’s mantle rises through the crust and erupts on the surface. This process occurs mainly at tectonic plate boundaries, such as convergent boundaries where plates collide and subduction occurs, and divergent boundaries where plates move apart. Hotspots, where plumes of magma rise from deep within the mantle, can also create volcanoes, as seen in Hawaii. The type of magma, its chemical composition, and the rate of eruption determine the nature of the volcano, influencing whether it forms broad shield volcanoes, steep stratovolcanoes, or smaller cinder cones. Understanding these processes helps scientists predict volcanic activity and assess potential hazards.
Types of Volcanic Activity and Eruption Styles
Volcanic eruptions vary greatly in style, from gentle lava flows to catastrophic explosive events. Effusive eruptions produce slow-moving lava that can cover large areas, creating fertile soil over time. Explosive eruptions, on the other hand, eject ash, gas, and pyroclastic material into the atmosphere, sometimes causing widespread destruction. Volcanoes can also produce lahars—dangerous mudflows triggered by volcanic ash mixing with water—and pyroclastic flows, which are fast-moving currents of hot gas and debris capable of obliterating everything in their path. By studying eruption patterns, scientists can classify volcanoes and assess the risks they pose to nearby communities and ecosystems.
Volcanoes and Climate: How Eruptions Influence Weather and Atmosphere
Volcanic eruptions have a significant impact on the Earth’s climate and atmosphere. Large eruptions can release sulfur dioxide and ash particles into the stratosphere, reflecting sunlight and temporarily cooling global temperatures. Historical examples, such as the eruption of Mount Tambora in 1815, led to the “Year Without a Summer,” causing crop failures and famine in parts of the world. Volcanoes also release greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide and water vapor, which can contribute to long-term climate change. Understanding these atmospheric effects is essential for predicting both immediate and long-term consequences of volcanic activity.
The Role of Volcanoes in Shaping Landscapes and Ecosystems
Volcanoes play a crucial role in shaping landscapes and creating habitats. Lava flows, ash deposits, and volcanic rocks gradually build mountains, plateaus, and islands. Over time, volcanic soil becomes highly fertile, supporting lush vegetation and diverse ecosystems. For example, the slopes of Mount Etna in Italy and the volcanic islands of Indonesia are home to rich biodiversity, demonstrating how volcanic landscapes foster life. Volcanoes also create geothermal features such as hot springs, geysers, and fumaroles, which support specialized organisms and attract scientific and touristic interest.
Historical Eruptions and Their Impact on Human Civilization
Throughout history, volcanic eruptions have profoundly influenced human societies. The eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD destroyed Pompeii and Herculaneum, preserving them as time capsules for archaeologists. The eruption of Krakatoa in 1883 caused tsunamis, killed tens of thousands of people, and affected global climate. Indigenous cultures often incorporated volcanoes into their mythology, viewing them as sacred or divine forces. Studying these historical eruptions provides insight into human resilience, disaster preparedness, and the social and economic consequences of volcanic activity.
Modern Volcanology and Monitoring Techniques
Today, volcanologists use advanced technology to monitor volcanoes and predict eruptions. Seismic activity, ground deformation, gas emissions, and satellite imagery help scientists assess volcanic risk in real-time. Early warning systems and evacuation plans save lives in areas near active volcanoes. Additionally, computer modeling allows researchers to simulate eruption scenarios and evaluate potential impacts on infrastructure, agriculture, and ecosystems. These modern tools reflect humanity’s growing understanding of volcanoes and our ability to coexist safely with these powerful natural features.
Volcanoes as Natural Laboratories
Volcanoes serve as natural laboratories for studying Earth’s processes. They provide insights into magma composition, tectonic activity, and the formation of minerals and rocks. Researchers study geothermal energy, volcanic gases, and lava chemistry to understand planetary processes and potential energy resources. Volcanoes on other planets, such as Mars and Venus, offer clues about extraterrestrial geology and the potential for life. By observing and analyzing volcanic activity, scientists deepen our understanding of Earth and the broader universe.
Conclusion: Appreciating the Fiery Giants of Our Planet
Volcanoes are more than destructive forces; they are architects of landscapes, regulators of climate, and catalysts of life and evolution. From their geological formation to their ecological and social impacts, volcanoes illustrate the dynamic and interconnected nature of our planet. Understanding their power, monitoring their activity, and appreciating their contributions to ecosystems and human culture allows us to coexist with these fiery mountains safely. By studying volcanoes, we gain knowledge, respect, and awe for the forces that shape life on Earth.